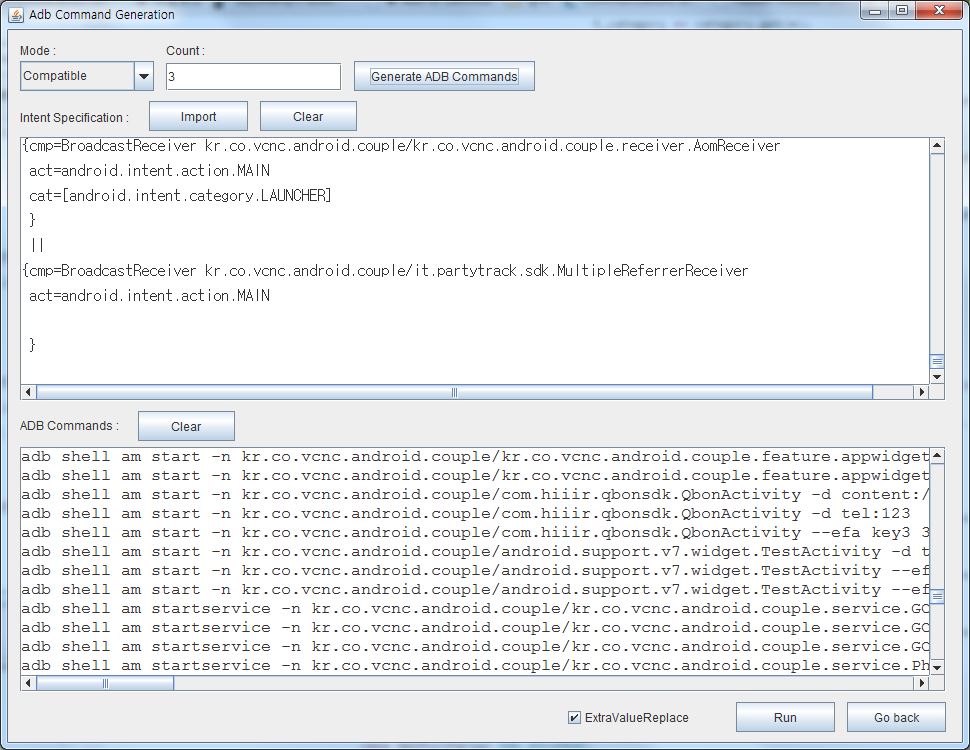
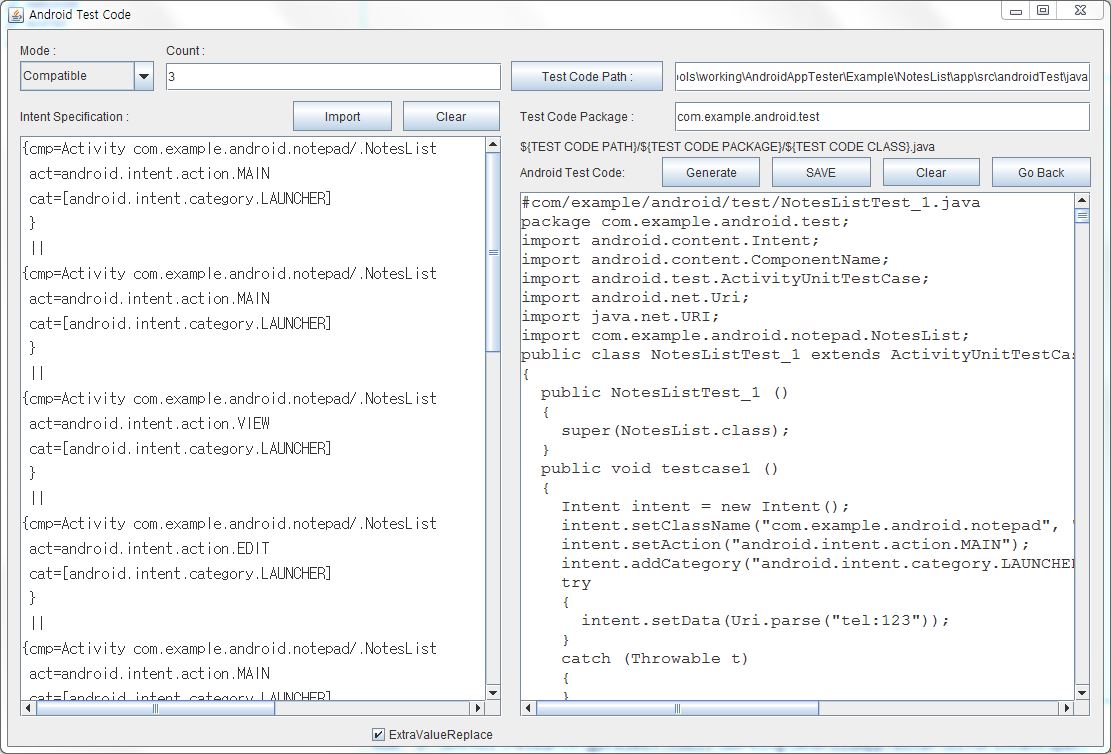
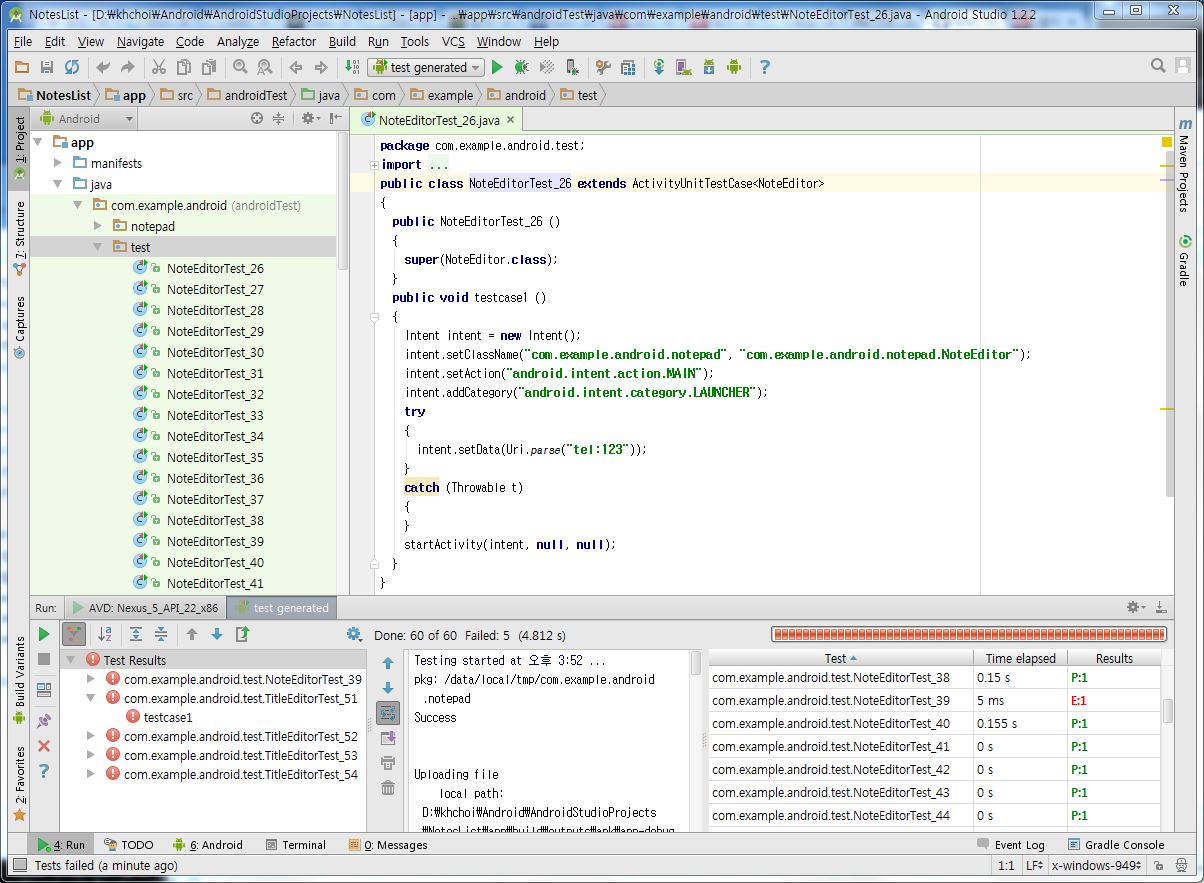
Programmers can write their own an intent specification manually or can import it from APK files or AndroidManifest.xml.
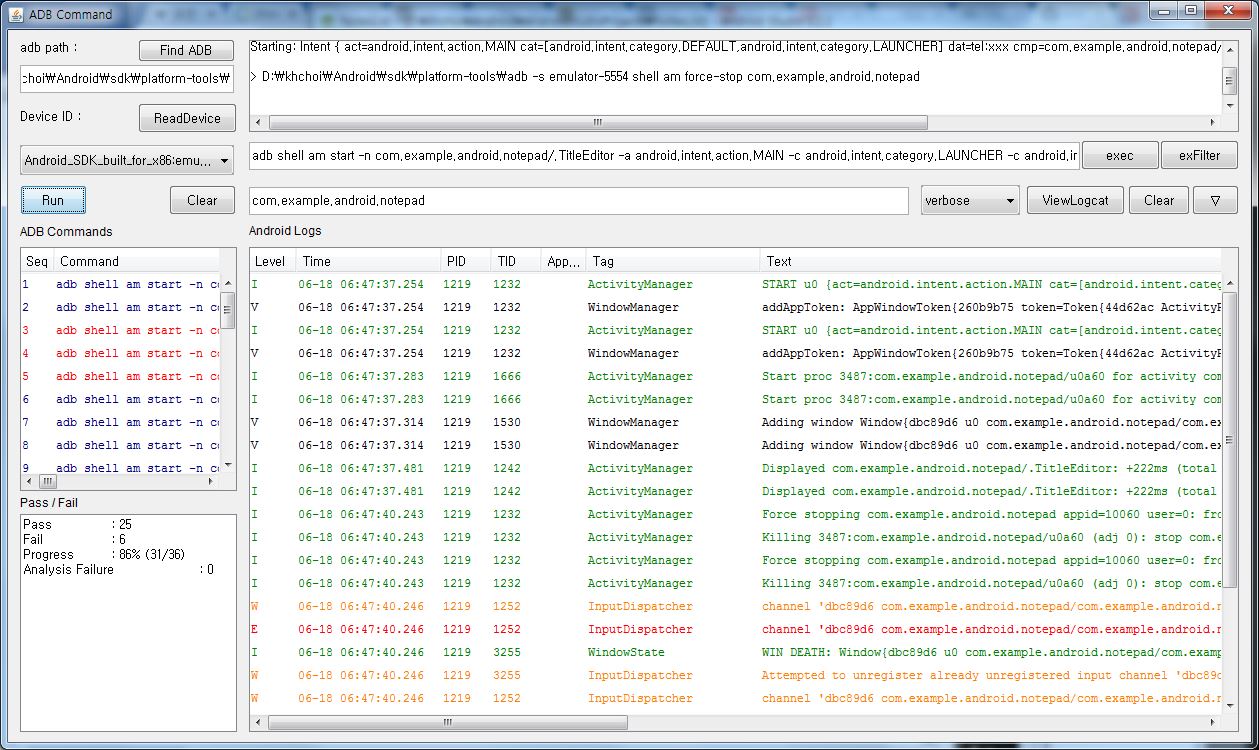
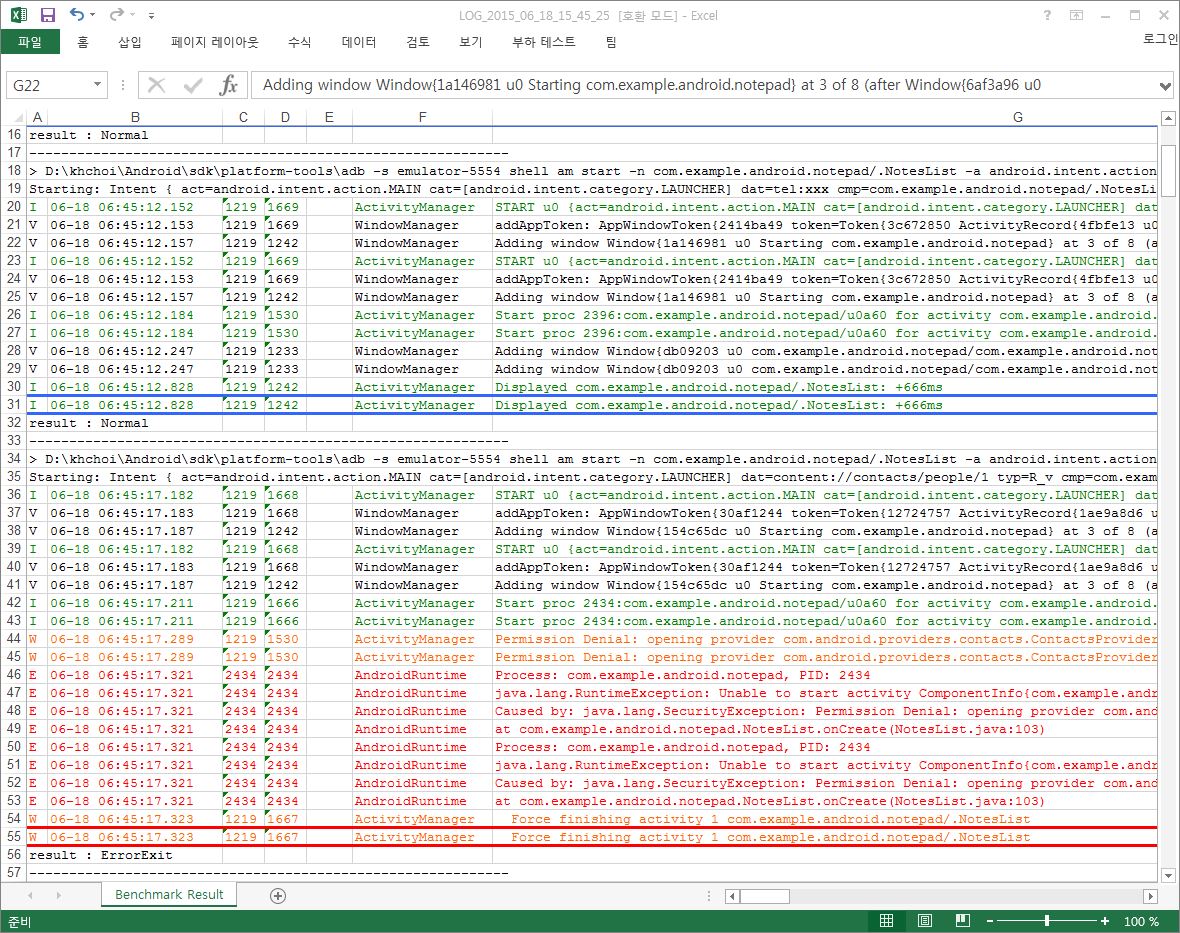
Once an intent specification is written, press either "ADB Command" button or "Android Test Code" button to generate the corresponding testing artifacts.